Poisson Regression | ||||
Description | Poisson Regression is a type of linear regression used to model the countable data. | |||
Why to use | For regression analysis of count data | |||
When to use | For numerical variables | When not to use | For textual variables | |
Prerequisites |
| |||
Input | Numerical variable which is countable. | Output |
| |
Statistical Methods used |
| Limitations | It can be used only on numerical data. | |
Poisson Regression is located under Machine Learning () under Regression, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Poisson Regression.
Properties of Poisson Regression
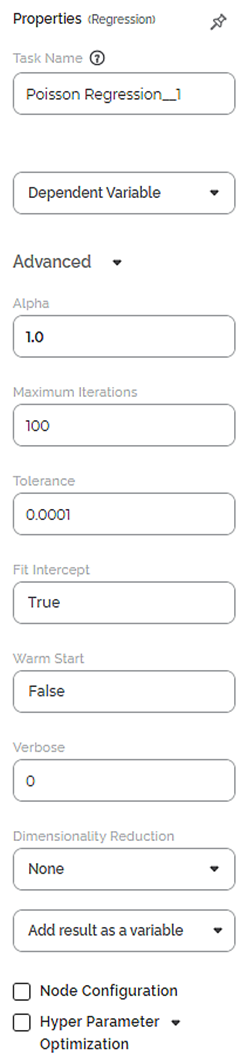
The available properties of the Poisson Regression are as shown in the figure below.
The table below describes the different fields present on the Properties pane of the Poisson Regression.
Field | Description | Remark | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Dependent Variable | It allows you to select the numerical variable on which the regression is to be applied. | You can select any numerical type of variable which contains count values. | |
Advanced | Alpha | It allows you to set the level of significance. | The default value is 1.0. |
Maximum Iterations | It allows you to enter the maximum number of iterations. | The default value is 100. | |
Tolerance | It allows you to enter the precision of the solution. |
| |
Fit Intercept | It allows you to select whether you want to calculate constant (c) value for your model. |
| |
Warm Start | It allows you to select whether you want to use the existing fitted model attributes to initialize the new model in the next call to fit. |
| |
Verbose | It allows you to select whether you want to enable logging. |
| |
Dimensionality Reduction | It allows you to select the method for dimensionality reduction. |
| |
Add result as a variable | It allows you to select the KPIs to be displayed in the output. | The available options are
| |
Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. | |
Hyper Parameter Optimization | It allows you to select the parameters for optimization. | For more details, refer to Hyperparameter Optimization. | |
Example of Poisson Regression
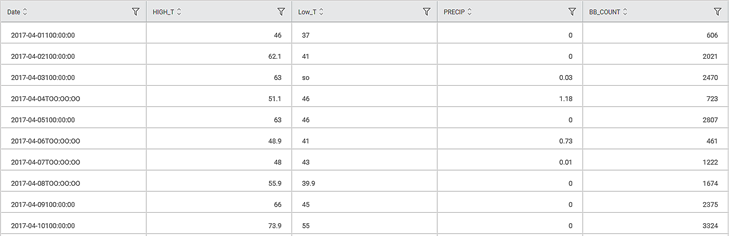
Consider a dataset of the count of the number of people crossing the Brooklyn Bridge on various dates. The dataset also contains data related to high and low temperatures and precipitation on those days. A snippet of input data is shown in the figure below.
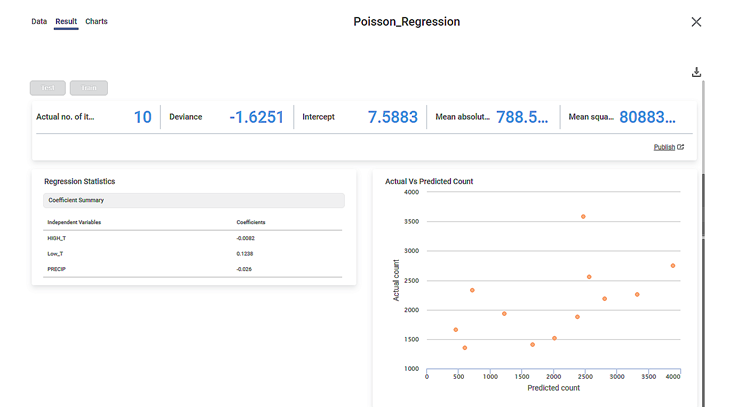
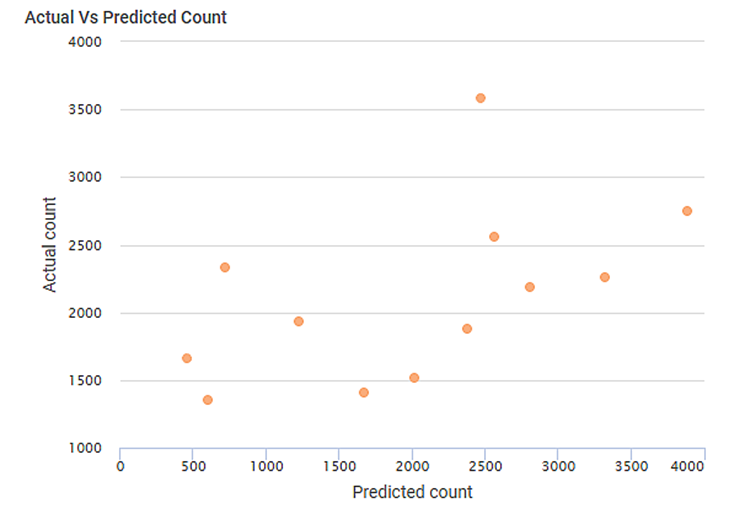
We select BB_Count as the Dependent Variable. The Result page of the Poisson Regression is displayed in the figure below.
As seen in the above figure, the KPIs for Poisson Regression, the Regression Statistics containing coefficients for the independent variables, and a scatter plot of Actual Vs Predicted count is displayed on the Result page.
When you hover over any point of the scatter plot, you see the Predicted Count and Actual Count values for the data point.
Table of Contents