Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function | |||
Description | Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function (ICDF) is the inverse of Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF). It helps to learn about the distribution of data by calculating the value associated with a specific cumulative probability in the dataset. | ||
Why to use | To determine the value of the variable or feature associated with a specific probability. | ||
When to use | For numerical variables having positive integer values. | When not to use | For numerical variables having values less than 0. |
Prerequisites |
| ||
Input | One numerical variable having values between 0 and 1. | Output |
|
Statistical Methods used |
| Limitations | It can be used only on numerical data. |
Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function is located under Model Studio ( ) in Statistical Analysis, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function.
The Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function determines the original value of the randomly selected variable for the given probability value from the dataset.
By default, the data is sorted and then sent to the algorithm. Also, in the output Data tab, the resultant data appears in a sorted manner.
Properties of Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function
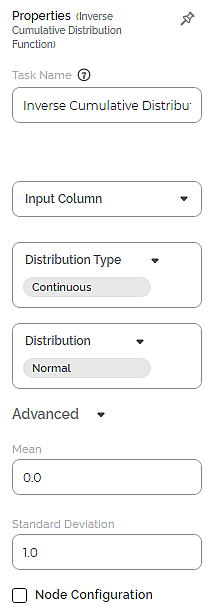
The available properties of the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function are as shown in the figure given below.
The table below describes the different fields present on the Properties pane of the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function.
Field | Description | Remark | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Input Column | It allows you to select the variable to be selected as the input attribute. |
| |
Distribution Type | It allows you to select the type of distribution to be applied to the data. | There are two types of Distribution to select from:
| |
Distribution | It allows you to select the sub-type of the Distribution selected above. | The sub-types present in Continuous and Discrete Distribution are given in Description of Advanced Options for Distribution Type and Distribution Pairs. | |
Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
In the Advanced options, algorithmic parameters for ICDF also appear according to the pair of Distribution Type and Distribution selected. These parameters change according to the Distribution Type and Distribution selected.
For example, when you select the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function node, the option for Distribution Type is Continuous and that for Distribution is Normal. In this case, the parameters that appear in the Advanced Options are Mean and Standard Deviation.
The table given below describes these two parameters.
Table: Description of Advanced Options for Continuous Distribution Type and Normal Distribution
Field | Description | Remark |
Mean | It allows you to select the mean value corresponding to the normal distribution. |
|
Standard Deviation | It allows you to select the value of standard distribution corresponding to the normal distribution. |
|
The table below gives the other parameters that appear in advanced options available for individual Distribution Types and Distribution pairs.
Table 6: Description of Advanced Options for Distribution Type and Distribution Pair for Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function
Distribution Type | Distribution | Parameter in Advanced Options | Description |
Continuous | Chi-squared | Degrees of Freedom |
|
Standard Exponential | — | The applicable parameters are already configured. | |
Exponential | Alpha (α) | You can select any real float value greater than zero. | |
F-distribution | Degree of Freedom 1 |
| |
Degree of Freedom 2 | |||
Gamma | Alpha (α) |
| |
Standard Normal | — | The applicable parameters are already configured. | |
Normal | Mean |
| |
Standard Deviation |
| ||
t | Degrees of Freedom |
| |
Standard Uniform | — | The applicable parameters are already configured. | |
Continuous Uniform | Lower Limit | The default value is 1. | |
Upper Limit |
| ||
Weibull_min | Shape Parameter |
| |
Weibull_max | Shape Parameter |
| |
Beta | Alpha |
| |
Beta |
| ||
cauchy | — | The applicable parameters are already configured. | |
lognormal | Sigma |
| |
Discrete | Binomial | Number of trials |
|
Probability |
| ||
Geometric | Probability |
|
Example of Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function
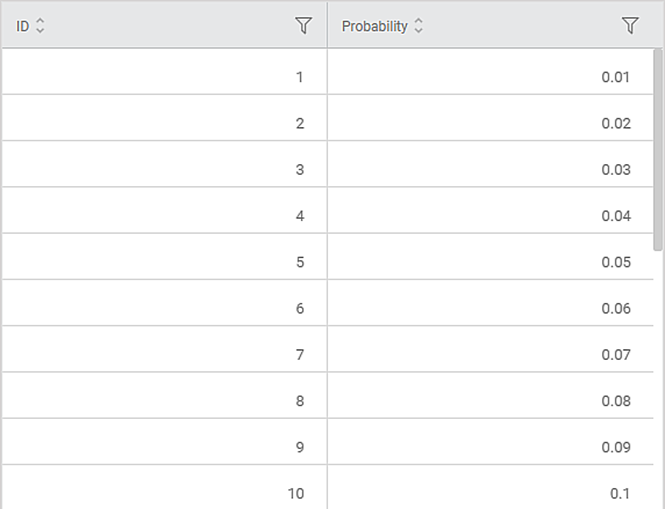
Consider a dataset of Probability values for various IDs. A snippet of input data is shown in the figure given below.
The selected values for properties of the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function are given in the table below.
Property | Value |
Input Column | Probability |
Distribution type | Continuous |
Distribution | Exponential |
Alpha | 1.0 |
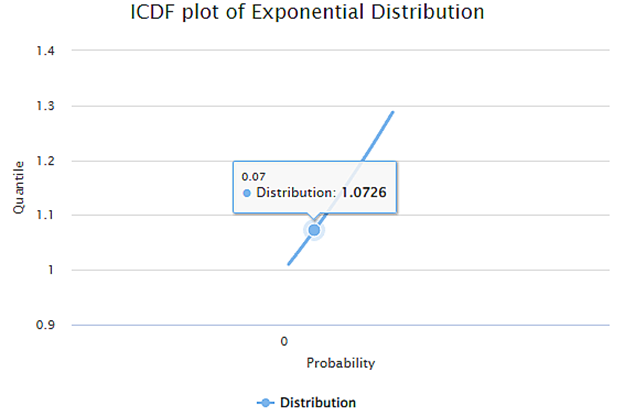
The Result page of the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function is displayed in the figure below. The graph shows the variation in Quartile values for the probability values in the dataset.
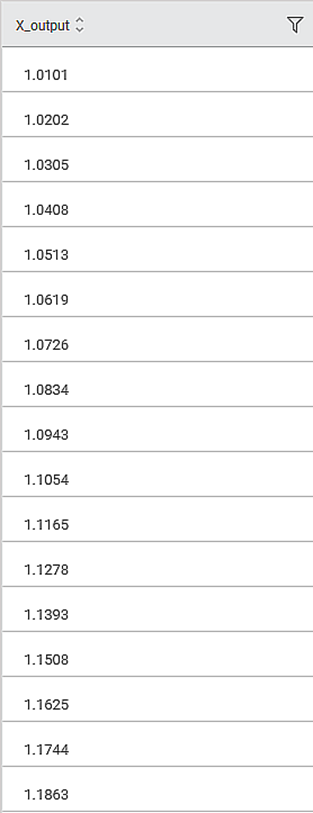
For example, the Probability for the data point 0.7 has a Quartile value of 1.0726.
The Data page of the Inverse Cumulative Distribution Function is displayed in the figure below. It shows a snippet of the X_output values, the Quartile values, corresponding to Probability values in tabular form. By default, the values of Petal Width are sorted and arranged in an ascending order.
Table of Contents