Parametric Distribution Fitting | ||||
Description | Parametric distribution fitting is the process used to select a statistical distribution that best fits a data set. | |||
Why to use | Statistical Analysis | |||
When to use | To decide the distribution best suited for data description. | When not to use | When the distribution of data is known. | |
Prerequisites | ||||
Input | A dataset containing continuous data. | Output | Best fit distributions sorted by the Goodness of Fit tests. | |
Statistical Methods used | — | Limitations | It can be used only on continuous data. It doesn’t work on categorical/textual data. | |
Parametric Distribution Fitting is located under Model Studio () in Statistical Analysis, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Parametric Distribution Fitting.
In Distribution fitting, first, the data is matched against probability distributions using parametric distribution-fitting. For each distribution, this fitting establishes a set of parameters that best describe the data characteristics. Next, one of the several Goodness-of-Fit tests is employed to determine the closeness of each fit. Finally, out of the results obtained, the highest-ranked fit is selected to represent the data.
Properties of Parametric Distribution Fitting
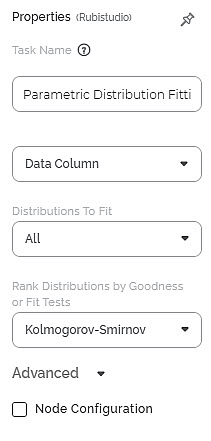
The available properties of Parametric Distribution Fitting are as shown in the figure given below.
The table given below describes the different fields present on the Properties pane of Parametric Distribution Fitting.
Field | Description | Remark | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Data Column | It allows you to select the column on which you want to apply Parametric Distribution Fitting. | Only a numerical column can be selected. | |
Distributions to Fit | It allows you to select the various distributions to fit the data. |
o Beta o Cauchy o Exponential o Exponentially modified Normal o Exponentiated Wiebull o F o Gamma o Log-normal o Logistic o Normal o Pearson type III o Uniform o Weibull maximum o Weibull minimum
| |
Rank Distributions by Goodness of Fit Tests | It allows you to rank the best fit distributions by the Goodness of Fit tests. |
o Kolmogorov-Smirnov o Chi square o Anderson Darling
| |
Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
Example of Parametric Distribution Fitting
Consider a dataset of a disk radius. A snippet of input data is shown in the figure given below.
The Properties selected for Parametric Distribution Fitting are shown in the table below.
Property | Value |
Data Column | radius |
Distributions to Fit | All |
Rank Distributions by Goodness of Fit Tests | Kolmogorov-Smirnov |
The various elements of the Result page are shown in the figures below.
The Result page displays Descriptive Statistics and Shapiro Wilk’s Test for Normality, as shown in the figure below.
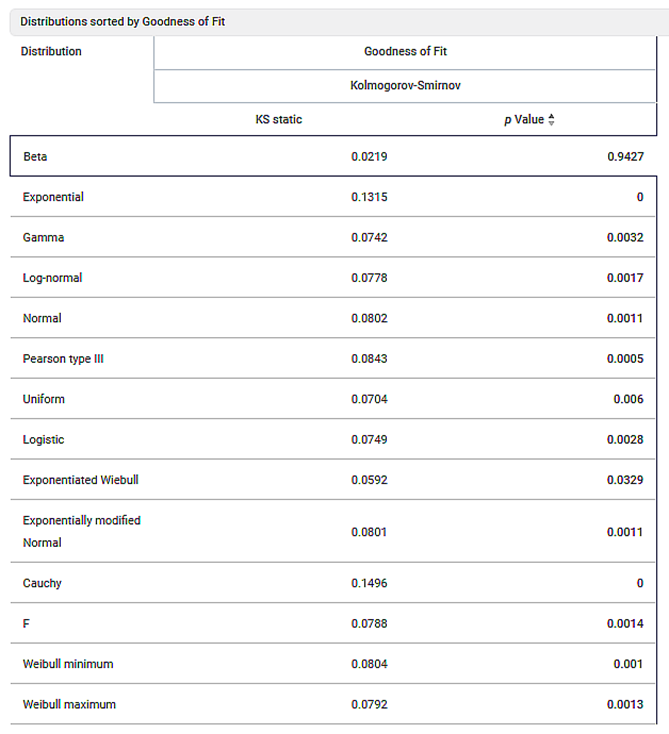
It also displays Distributions sorted by the Goodness of Fit scores, as shown in the figure below.
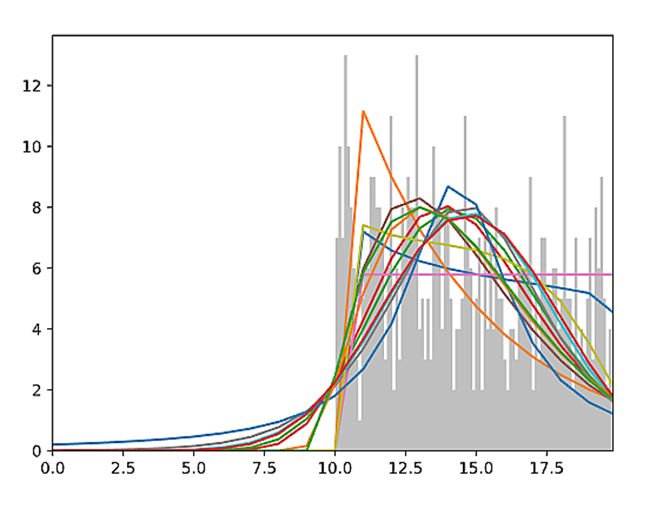
A Histogram of the frequency of values for the selected column with Sample Distribution and Beta Distribution is also displayed.
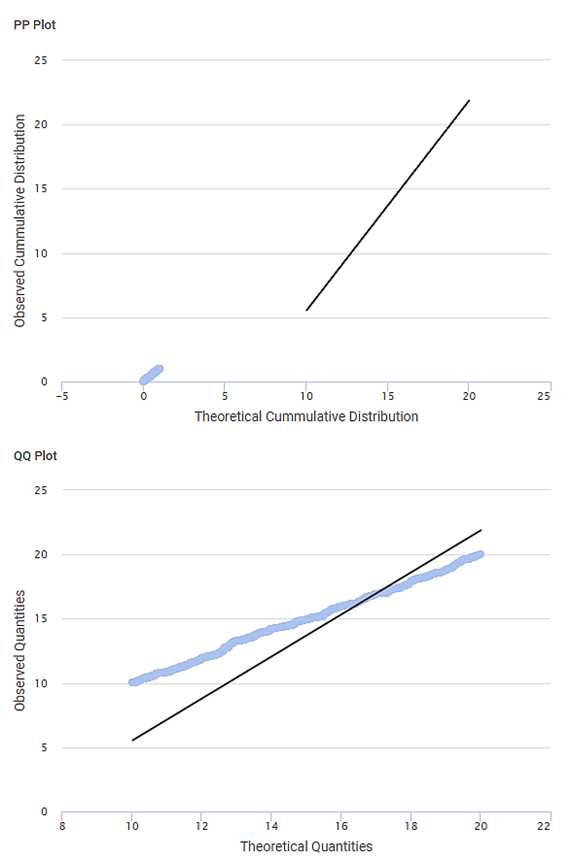
The Result page also displays PP Plot and QQ Plot, as shown in the figure below
PP Plot (Probability-Probability Plot) is a probability plot to assess how closely two datasets agree. It plots the two cumulative distribution functions against each other. PP Plots are used to evaluate the skewness of a distribution.
QQ Plot (Quartile-Quartile Plot) is a plot of two quartiles against each other. A quartile is a fraction where certain values of the dataset fall below that quartile and certain values are above it. Thus, QQ Plot shows the percentiles of a standard normal distribution against the corresponding percentile of the observed data.
Some important points about Parametric Distribution Fitting -
- This feature helps you to determine which Distribution fits best on your data.
- The distributions are sorted by the highest values of the p-value for the selected test.
- Not all distributions have the same set of parameters.
- Anderson Darling test to be used only with these distributions – Normal, Exponential, and Logistic.
Table of Contents