| Data Unpivot | |||
Description |
| ||
Why to use | To transform the column data into row data | ||
When to use | When you want to transform the data type | When not to use | — |
Prerequisites | Data containing multiple columns | ||
Input | A supervised data or any data in row-column format | Output | Unpivoted data with column data converted to row data |
Statistical Methods used | — | Limitations | — |
Data Unpivot is located under Model Studio ( ) in Data Preparation, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Data Unpivot.
Properties of Data Unpivot
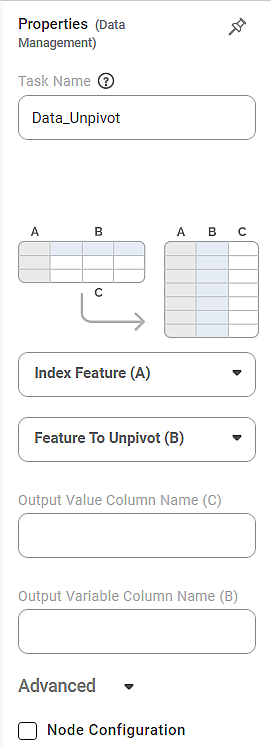
The available properties of Data Unpivot are shown in the figure below.
The depictions of tables and the change from one table structure to another are shown in the figure above. The elements A, B, and C of the first table are rearranged as shown in the second table.
The table below describes different fields present on the properties of Data Unpivot.
Field | Description | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the task's name as required. | |
Index Feature (A) | It allows you to select the variable(s) to be selected for the first column of the resultant table. | You can select a single or multiple variables. | |
Feature to Unpivot (B) | It allows you to select the variable(s) to be selected for the second column of the resultant table. |
| |
Output Value Column Name (C) | It allows you to enter the Name to be given to the third column of the resultant table. |
| |
Output Variable Column Name (B) | It allows you to enter the Name to be given to the second column of the resultant table. |
| |
Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
Example of Data Unpivot
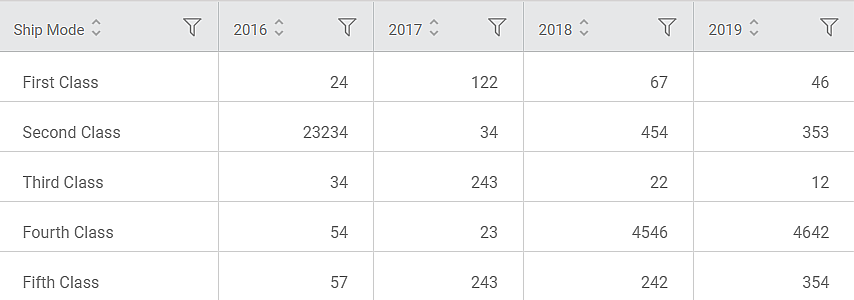
Consider a Ship Mode dataset containing dispatch data for five consecutive years, shown in the figure below.
We select the following properties and apply Data Unpivot.
Index Feature (A) | Ship Mode |
Feature to Unpivot (B) | 2016 and 2017 |
Output Value Column Name (C) | Values |
Output Variable Column Name (B) | Year |
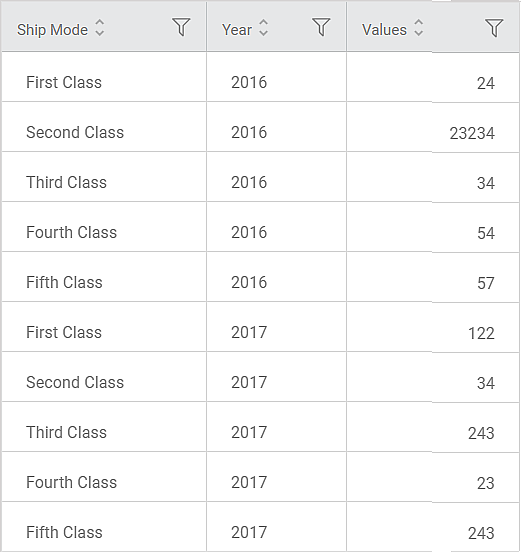
The figure below shows the resultant Unpivoted table on the Data tab.
You can see that the table structure has changed. The values for Year and Value variables are displayed, for all Ship Modes, one below the other.
Table of Contents