Descriptive Statistics | |||||
Description | Descriptive statistics involves the calculation of various statistical measures such as the measure of central tendency, the measure of variability, percentiles, and also the diagrammatic & graphical representation of data. | ||||
Why to use | To prove simple summaries about the sample data and its measures. | ||||
When to use |
| When not to use | On textual data. | ||
Prerequisites | It should be used on numerical data. | ||||
Input | Any dataset that contains numerical data. | Output | Statistical information of the selected features is displayed. | ||
Statistical Methods used |
| Limitations | - | ||
Descriptive Statistics is located under Model Studio ( ) in Data Preparation, in the task pane on the left. Use drag-and-drop method to use algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Descriptive Statistics.
Descriptive statistics are brief descriptive coefficients that summarize a given data set, which can be either a representation of the entire or a sample of a population. Descriptive statistics are broken down into measures of central tendency and measures of variability (spread).
Measures of Frequency: Count, Percent, and Frequency
Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Median, and Mode
Measures of Dispersion or Variation: Range, Variance, Standard Deviation
Measure of lack of symmetry: Skewness
Measure of tailedness: Kurtosis
Measure of the statistical accuracy: Standard error
Partition Values: Percentile Ranks, Quartile Ranks.
Properties of Descriptive Statistics
The available properties of Descriptive Statistics are as shown in the figure given below.
The table given below describes different fields present on properties of Descriptive Statistics.
Field | Description | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|
Task Name | It displays the name of the selected task. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Features | It allows you to select the features for which you want to get statistical information. |
| |
| Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
Interpretation from Descriptive Statistics
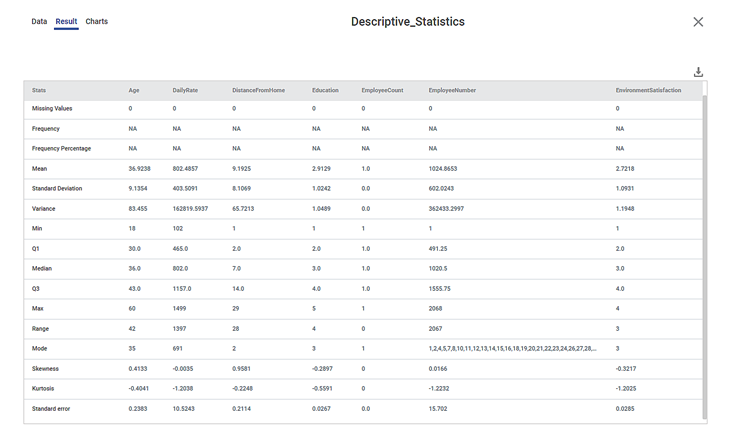
The figure given below displays the output of descriptive statistics used on sample data.
The table given below describes the result for Descriptive Statistics.
Descriptive Statistic | Result | Remark |
|---|---|---|
Total No. of Observations | It provides the total number of observations present in the dataset | It is the total count of the number of rows. |
Missing | It shows the number of missing values present in the selected features. | You cannot build some models if data contains missing values. |
Frequency | It provides the frequency of the number of times the data has occurred. | It is calculated only for categorical datatype. |
Frequency Percentage | It provides the frequency percentage of the number of times the data has occurred. | It is calculated only for categorical datatype. |
Mean | It provides average of the selected features. | It is calculated only for numerical datatype. |
Standard Deviation | It measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean. |
|
Variance | It measures how far a set of numbers are spread out from their average value. |
|
Min | It provides the minimum value for the selected features. | It is calculated only for numerical datatype. |
Q1 | It provides the 25th percentile of the data. |
|
Median (Q2) | It provides the middle value for the selected features. |
|
Q3 | It provides the 75th percentile of the data. |
|
Max | It provides the maximum value for the selected features. | It is calculated only for numerical datatype. |
Range | It is the difference between maximum and minimum value. | It is calculated only for numerical datatype. |
Mode | It provides the value that has occurred maximum times. |
|
Skewness | It provides the distribution of data points.
|
In other words,
|
Kurtosis | It identifies whether the tails of a given distributed data contain extreme values. |
|
Standard error | It represents the standard deviation of the mean within a dataset. It provides a measurement for the spread of data. |
|
Table of Contents