Data Pivot | |||
Description |
| ||
Why to use | To transform the row data into column data | ||
When to use | When you want to transform the data type | When not to use | — |
Prerequisites |
| ||
Input | Any type of dataset containing rows and columns | Output | Pivoted data with row data converted to column data |
Statistical Methods used | — | Limitations | — |
Data Pivot is located under Model Studio ( ) in Data Preparation, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm on the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Data Pivot.
Properties of Data Pivot
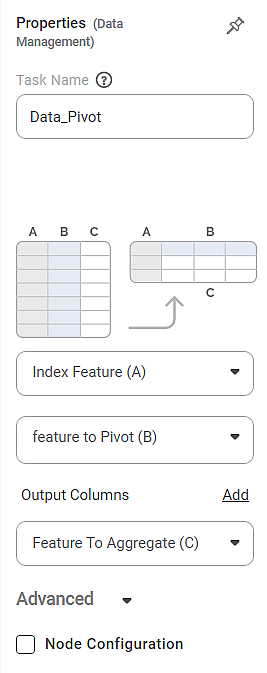
The available properties of Data Pivot are shown in the figure below.
The depictions of tables and the change from one table structure to another are shown in the figure above. The elements A, B, and C of the first table are rearranged as shown in the second table.
The table below describes different fields present on the properties of Data Pivot.
Field | Description | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. |
| |
Index Feature (A) | It allows you to select the variable to be selected for the first column of the resultant table. |
| |
Feature to Pivot (B) | It allows you to select the variable(s) to be selected for the remaining columns of the resultant table. |
| |
Unique values of features to Pivot | It allows you to select unique variable values as column names in the resultant table. |
| |
Feature to Aggregate (C) | It allows you to select the variable to be aggregated based on the variable selected as Feature to Pivot (B). |
| |
Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
Example of Data Pivot
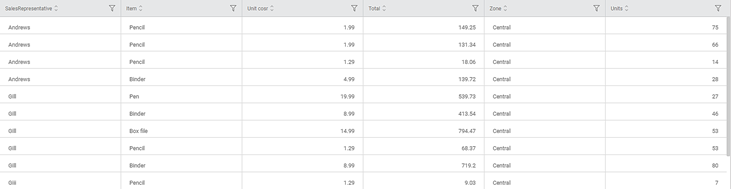
Consider a NewSalesData dataset containing information on the zone-wise sale of items by various sales representatives along with the unit cost and total. A snippet of the input data is shown in the figure below.
We select the following properties and apply Data Pivot.
Index Feature (A) | Item |
Feature to Pivot (B) | Zone |
Output Columns (unique values) | Central, East, and West |
Feature to Aggregate (C) | Total (Average) |
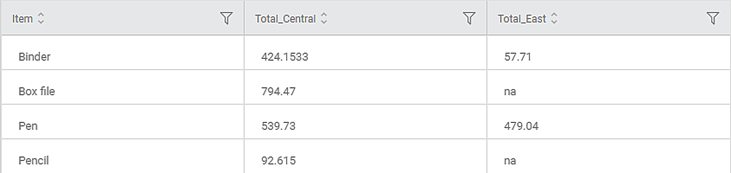
The figure below shows the resultant Pivoted table on the Data tab.
You can see that
- The table structure has changed from simple to cross, that is from a tall table to a wide one.
- The Total values are aggregated in second, third, and fourth columns by mean, for Central and East zones, respectively.
Table of Contents