Lookup | |||
Description | Lookup helps you to match values of specified fields in two data sources. | ||
Why to use | To compare values in data sources. | ||
When to use | To determine the presence of a particular field from one data source in another data source. | When not to use | When the data sources do not contain any common fields. |
Prerequisites | No prerequisites; it can be applied to any data source. | ||
Input | Two data sources containing one or more common fields. | Output | Based on the option selected for the If non matching records found? property, matching/non-matching records are returned, or task fails. |
Statistical Methods used | — | Limitations | No limitations; it can be applied to any data. |
Lookup is located under Model Studio () in Data Preparation, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the feature in the canvas. Click the feature to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Lookup.
The Lookup functionality in Rubiscape allows you to connect two data sources and compare them based on certain conditions.
Lookup checks all the values in the given data sources and matches the records from one data source to another for the selected fields.
Lookup is not a stand-alone activity; it is to be connected to a predecessor. The predecessor can be a dataset or output obtained from any data pre-processing node. In the Lookup properties, you can specify the dataset to which you want to compare the values of the predecessor of Lookup.
Properties of Lookup
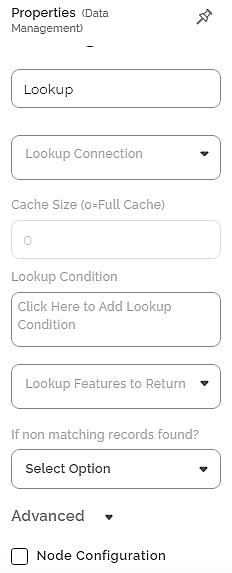
The available properties of the Lookup are as shown in the figure given below.
The table given below describes the different fields present on the properties of the Lookup.
Field | Description | Remark | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Lookup Connection | It allows you to select the dataset to compare with the predecessor of Lookup. |
| |
Cache Size | It is set to 0 by default. | — | |
Lookup Condition | It allows you to add the condition to compare the values. | Refer to Adding Lookup Condition. | |
Lookup Features to Return | It allows you to select the features that are the columns of the data set selected in Lookup Connection. These features are added to the result of Lookup. |
| |
If non matching records found? | It allows you to select the action to be taken if non-matching records are found. | The available options are –
| |
Advanced | Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control on the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. |
Adding Lookup Condition
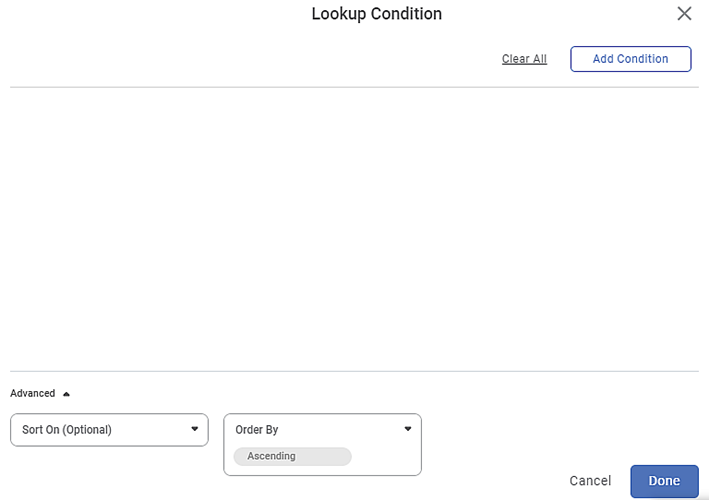
To add a lookup condition, follow the steps given below.
- In the Properties pane, click Lookup Condition.
Lookup Condition page is displayed. - Click Add Condition.
- From the Lookup Feature drop-down, select a feature of the lookup dataset.
From the Condition drop-down, select the comparison operator.
Note:
The available operators are <, <=, <>, =, >, and >=.
- From the Input Feature drop-down, select a feature of the input data source (the predecessor node of Lookup).
- Additionally, from the Sort On drop-down, select the feature to sort the data. This step is optional.
From the Order By drop-down, select the ordering option – Ascending or Descending. This step is optional. The default value is Ascending.
The complete dataset selected for the lookup feature is ordered accordingly.Note:
To add more conditions, repeat steps 2 to 7. If more than one query is added, they are joined using the logical AND operator.
- Click Done.
The specified conditions are added. If you have more than one condition, they are joined using the logical AND operator.
Example of Lookup
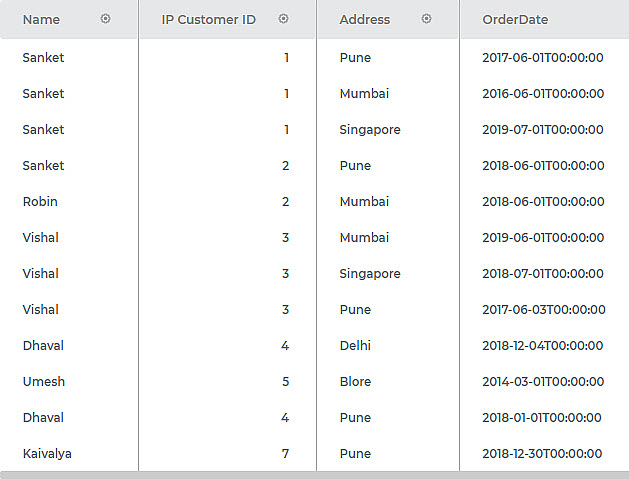
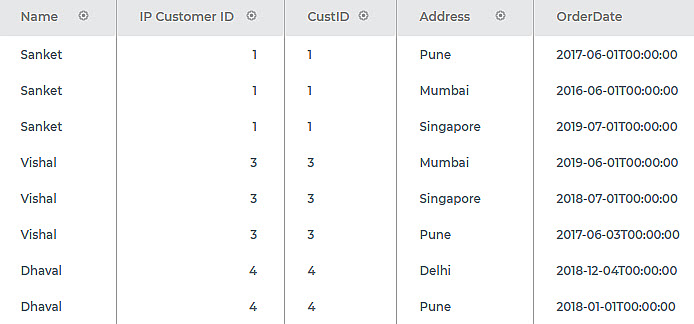
Consider a dataset Customer Order with the Customer ID, Name, Address, and OrderDate columns. The input data is shown in the figure below.
Figure: Input Data Snippet
The Lookup dataset - Customer Billing with CustID and Billing Date columns is shown in the figure below.
To lookup for customer id in the Billing Dataset, the Lookup properties are selected as below.
Property | Value |
Lookup Connection | Customer Billing (A dataset containing CustID and BillingDate as shown in Figure 5) |
Lookup Condition | CustID = IP Customer ID |
Lookup Features to Return | CustID |
If non matching records found? | Capture Non Matching Records |
The result of the Lookup for Capture Non Matching Records is displayed in the figure below.
Figure: Output of Lookup – Capture Non Matching Records
As seen in the above figure, the non-matching records are captured, and their Lookup_Flag value is 0.
If the property If non matching records found? is set to Do Not Pass, the result is displayed as shown in the figure below.
Figure: Output of Lookup – Do Not Pass Non Matching Records
As seen in the above figure, the non-matching records (2, 5, and 7) are not passed to the output.
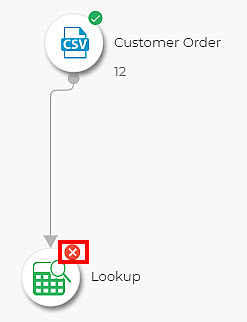
If the property If non matching records found? is set to Fail Task, the Lookup task fails as the datasets contain non-matching records. The Lookup task fails, as shown in the below figure.
Figure: Failed Lookup Task
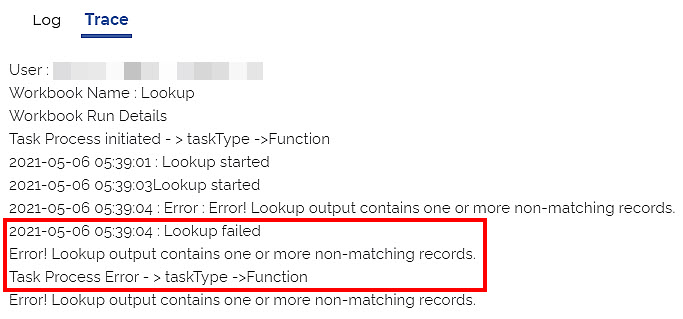
The Trace Log displays an error, as shown in the figure below.
Figure: Trace Log for Failed Lookup Task
Table of Contents