When the Rubiscape platform is deployed on any instance, the configuration for that instance is monitored and modified using the Settings page. As an administrator, you can visit the Settings page to perform various configuration handling tasks.
Rubiscape provides settings support for the following options.
- General
- Storage
- Cache
- Auto Scaling
- Organization
These settings are
- Common for all tenants
- Accessible by super admin, root admin, and tenant admins
- Either instance-level or tenant-level (depending on their functioning)
The following sections discuss each of these settings in detail.
General Settings
General settings are applicable at the instance level.
These settings are useful for
- Any kind of scheduling activity. For example, scheduling a Workflow or a Dashboard.
- Running the SSAS and Jupyter URLs
The following table explains various fields in General settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
SMTP Server | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Server. |
|
SMTP Port | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Port |
|
Sender Email ID | Enter the email address you wish to be the default sender ID for all the scheduling purposes. | The Sender Email ID is used
|
Sender Email Password | Enter a valid email password for the above email ID. |
|
SSAS URL | SQL Server Analysis Services Uniform Resource Locator |
|
Jupyter URL | Jupyter Uniform Resource Locator |
|
|
|
Storage Settings
In Rubiscape, the storage settings are at the instance level. Currently, Rubiscape supports five types of storage. You can select any storage as required.
- Local (default)
- S3 on AWS
- MinIO
- Azure Blob Storage
- Google Cloud Platform
The following sections explain these storage types in detail.
Local
Local storage is the default storage for Rubiscape.
It requires no additional inputs.
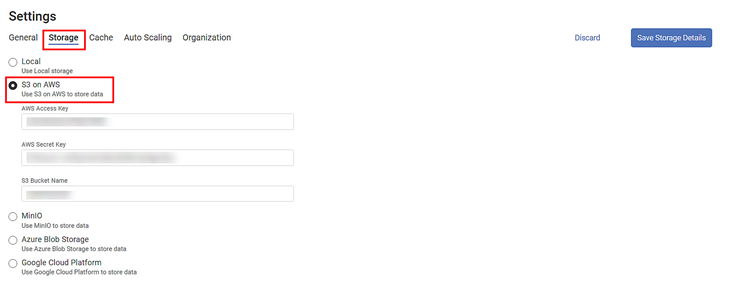
S3 on AWS
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a public cloud object storage service that stores data as objects within buckets. The object is a combination of a file and its metadata. Buckets are containers to store these objects.
The S3 on AWS storage contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in S3 on AWS settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
AWS Access Key | Enter the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Key. |
|
AWS Secret Key | Enter the secret key to sign requests. |
|
S3 Bucket Name | Enter a suitable name for the S3 storage container. |
|
MinIO
MinIO is an open-source distributed object storage server. It comes with an S3 storage functionality designed for private cloud infrastructure. MinIO is one of the best servers for storing unstructured data (images, videos, log files, backups, and containers).
The MinIO storage contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in MinIO settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
MinIO Access Key | Enter the MinIO Access Key to authenticate the user. |
|
MinIO Secret Key | Enter the MinIO Secret Key to authenticate the user. | It is a unique key and equivalent to a password. |
MinIO Host | Enter a valid IP address to connect to the MinIO host server. | The hostname needs to include the port. |
MinIO Bucket Name | Enter a valid MinIO bucket name |
|
Azure Blob Storage
Azure Blob (Binary Large Object) Storage is Microsoft's cloud-based object storage solution. It is an optimized storage facility to store a huge amount of unstructured, text, and binary data.
The Azure Blob Storage contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Azure Blob Storage settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
Default Endpoint Protocol | Enter the default endpoint protocol HTTPS, which is the default for Azure. |
|
Account Name | Enter the account name for the Azure storage. | It is user-specific. |
Account Key | Enter the account key for the Azure storage | It is user-specific. |
Endpoint Suffix | Enter the endpoint suffix for the Axure storage. | The default endpoint suffix is core. |
Blob Storage Container Name | Enter a suitable blob storage name for the Azure storage bucket. | – |
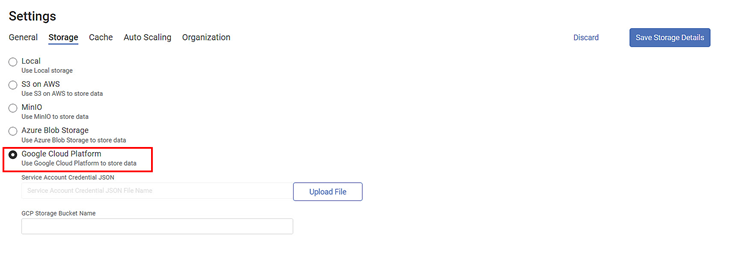
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform provides an object storage facility to companies of all sizes and data generation capacity. You can store and retrieve data as and when you want.
The Google Cloud Platform contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Azure Blob Storage settings.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Service Account Credential JSON | Click Upload File to upload the JSON file containing the service account credentials. |
GCP Storage Bucket Name | Enter a suitable name for the Google Cloud Platform storage container name. |
|
|
Cache
In Rubiscape, the cache settings are at the instance level. Currently, Rubiscape supports six types of caches. You can select any caching method as required.
- Django
- Redis
- S3 on AWS
- MinIO
- Azure Blob Storage
- Google Cloud Platform
The following sections explain these storage types in detail.
Django
Django is the default storage for Rubiscape cache.
It requires no additional inputs.
Redis
Redis is an open-source in-memory data structure store used as a cache in Rubiscape.
The Redis cache contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Redis cache settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
Redis Cache Host | Enter the cache host on which the Redis cache is stored. | Usually, the cache is stored on the localhost. |
Redis Cache Port | Enter the cache port to which the Redis cache is connected. | The default Redis cache port is 6379. |
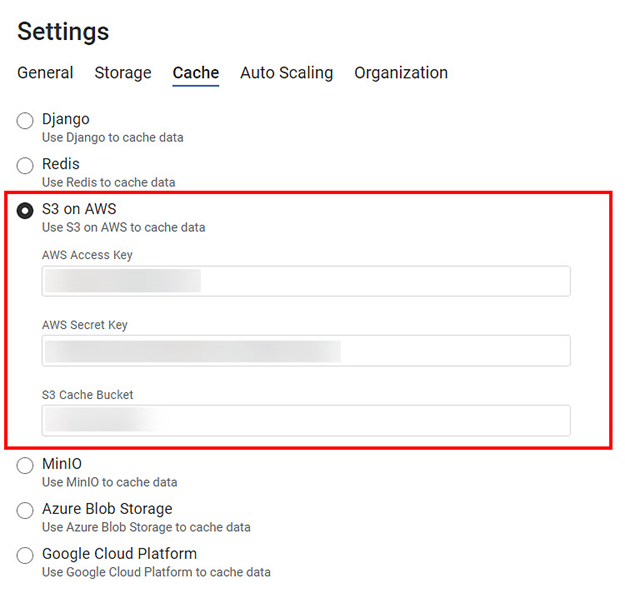
S3 on AWS
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a public cloud object storage service that stores data as objects within buckets. The object is a combination of a file and its metadata. Buckets are containers to store these objects.
The S3 on the AWS cache contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in S3 on AWS settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
AWS Access Key | Enter the AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) Key. |
|
AWS Secret Key | Enter the secret key to sign requests. |
|
S3 Cache Bucket | Enter a suitable name for the S3 cache container. |
|
MinIO
MinIO is an open-source distributed object storage server. It comes with an S3 storage functionality designed for private cloud infrastructure. MinIO is one of the best servers for storing unstructured data (images, videos, log files, backups, and containers).
The MinIO cache contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in MinIO settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
MinIO Access Key | Enter the MinIO Access Key to authenticate the user. |
|
MinIO Secret Key | Enter the MinIO Secret Key to authenticate the user. | It is a unique key and equivalent to a password. |
MinIO Host | Enter a valid IP address to connect to the MinIO host server. | The hostname needs to include the port. |
MinIO Bucket Name | Enter a valid MinIO bucket name |
|
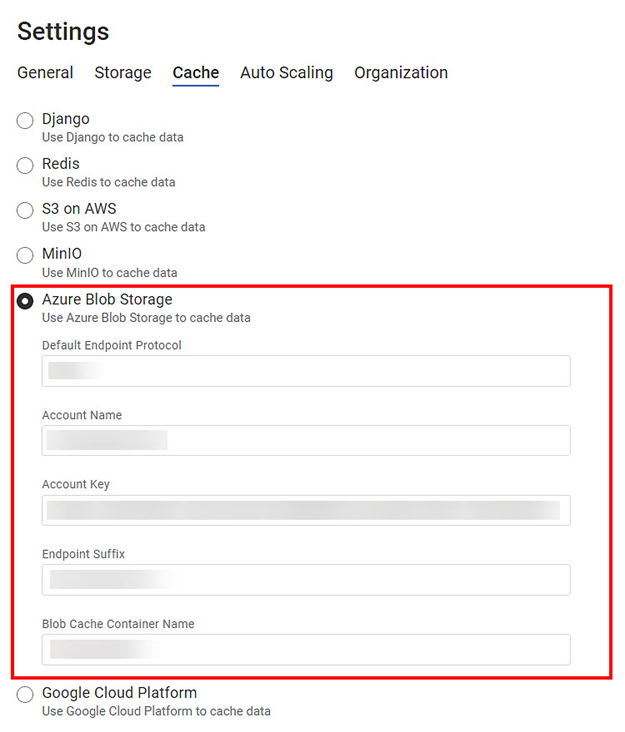
Azure Blob Storage
Azure Blob (Binary Large Object) Storage is Microsoft's cloud-based object storage solution. It is an optimized storage facility to store a huge amount of unstructured, text, and binary data.
The Azure Blob cache contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Azure Blob cache settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
Default Endpoint Protocol | Enter the default endpoint protocol HTTPS, which is the default for Azure. |
|
Account Name | Enter the account name for the Azure cache. | It is user-specific. |
Account Key | Enter the account key for the Azure cache. | It is user-specific. |
Endpoint Suffix | Enter the endpoint suffix for the Axure cache. | The default endpoint suffix is core. |
Blob Cache Container Name | Enter a suitable blob cache name for the Azure cache bucket. | – |
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform provides an object storage facility to companies of all sizes and data generation capacity. You can store and retrieve data as and when you want.
The Google Cloud Platform contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Azure Blob Cache settings.
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Service Account Credential JSON | Click Upload File to upload the JSON file containing the service account credentials. |
GCP Storage Bucket Name | Enter a suitable name for the Google Cloud Platform cache container name. |
|
|
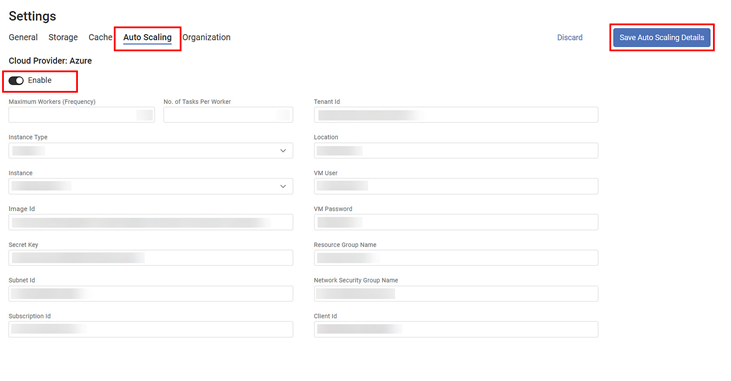
Autoscaling
Autoscaling is a cloud computing technique for scaling cloud-based services and dynamically allocating computational resources. Depending upon the user needs, server traffic, and load on a server, the active number of servers (typically called workers) varies automatically. Typically, several workers are activated simultaneously as required when the load peaks, while when there is no substantial traffic on a server, the workers are scaled down (switched off). Hence, the only optimum number of workers are active at any time.
In Rubiscape, the autoscaling settings are tenant-specific. As you change the tenant, these settings also change. It may so happen that one of your projects with a specific workload is handled through one tenant. Hence, separate settings may be required and can be configured for separate tenants.
Currently, two scenarios are possible related to auto-scaling in Rubiscape.
Auto-scaling disabled:
- NO auto-scaling
- Worker node configurations are default and are decided by the admin
Auto-scaling enabled:
Rubiscape provides support for the following two cloud providers:
- Microsoft Azure
- AWS
The following four drop-downs are the same for Microsoft Azure and AWS.
- Maximum Workers (Frequency)
- No. of tasks per worker
- Instance Type
- Instance
|
|
The following sections discuss the two cloud providers in detail.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
The AWS cloud provider contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in AWS cloud provider settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
|---|---|---|
Maximum Workers (Frequency) | Enter the maximum number of tasks that can be run simultaneously on a worker. |
|
No. of Tasks Per Worker | Enter the number of tasks you want to run at a time on each worker. |
|
Instance Type | Select the instance type from the drop-down. | Options:
|
Instance | Select the instance based on the instance type and the computational power required. |
|
Image Id | Enter the Amazon Machine Image (AMI) ID to launch the instance. |
|
Secret Key | Enter the secret key to launch the instance. | It is like a password. |
Subnet Id | Enter the Subnet ID to access a range of IP addresses in your Virtual Private Cloud. |
|
Region Name | Enter the name of the physical location where your data center (also called the Availability Center) is located. |
|
Security Group Ids | Enter the security group IDs for your EC2 instance. |
|
Access Key | Enter your unique user or account identifier key for AWS |
|
Key Name | Enter the key name to identify a particular object in the S3 bucket. |
|
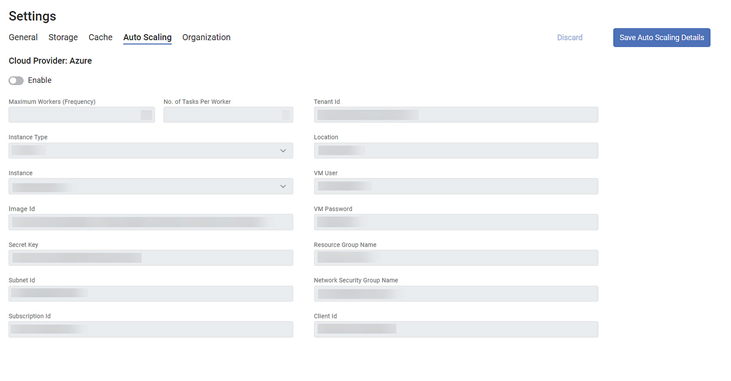
Microsoft Azure
The Azure cloud provider contains the following fields.
The following table explains various fields in Azure cloud provider settings.
Field | Description | Remark |
Maximum Workers (Frequency) | Enter the maximum number of tasks that can be run simultaneously on a worker. |
|
No. of Tasks Per Worker | Enter the number of tasks you want to run at a time on each worker. |
|
Instance Type | Select the instance type from the drop-down. | Options:
|
Instance | Select the instance based on the instance type and the computational power required. |
|
Image Id | Enter the Azure Image ID to launch the instance. |
|
Secret Key | Enter the secret key to launch the instance. | It is like a password. |
Subnet Id | Enter the Subnet ID to access a range of IP addresses in your Virtual Private Cloud. |
|
Subscription Id | Enter a unique alphanumeric string to identify your Azure subscription. |
|
Tenant Id | Enter your global unique identifier (GUID). |
|
Location | Enter the location of your data center. |
|
VM User | Enter your Virtual Machine Administrator User name. |
|
VM Password | Enter the password for your Virtual Machine Administrator User. | – |
Resource Group Name | Enter a name for your resource group. |
|
Network Security Group Name | Enter the name of the network security group. |
|
Client Id | Enter your application ID with Azure. |
|
|
|
Organization
The organization settings are read-only settings where you can add the organization's name, a linear logo, and a small icon.
The permissible size for
- Linear logo: 97 px (width) by 40 px (height)
- Small Icon: 40 px (width) by 40 px (height)
The following image formats are supported to upload the linear logo and small icon.
- PNG
- JPG
- JPEG
Table of Contents