Incremental Learning | |||||
Description | Incremental Learning processes the data one element at a time against batch methods that work on the entire set of data at a time. It usually stores a small number of elements, such as a constant number, in contrast to batch methods that store all the data. | ||||
Why to use | It generates an explicit knowledge structure that describes the clustering in a way that can be visualized and reasoned about. | ||||
When to use |
| When not to use | When data is non-spherical. | ||
Prerequisites | Input data should be of text type and should not contain special characters and numbers. | ||||
Input | Textual Data | Output | Data divided into clusters | ||
Statistical Methods used | Limitations |
| |||
Incremental Learning is located under Textual Analysis ( ) in Clustering, in the left task pane. Use the drag-and-drop method to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Refer to Properties of Incremental Learning.
The incremental learning algorithm uses new input data to train the model continuously and enrich its knowledge. It is used when the training data is available periodically, or the data size is beyond the system memory limit.
This algorithm processes the data, taking one element at a time. They store a small number of elements like a constant number.
It is one of the best algorithms in terms of execution time, space, number of I/O operations, and accuracy.
Properties of Incremental Learning
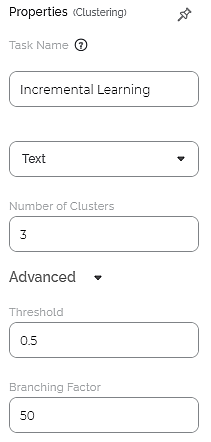
The available properties of Incremental Learning are as shown in the figure given below.
The table given below describes the different fields present on the properties of Incremental Learning.
Field | Description | Remark | |
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. | You can click the text field to edit or modify the name of the task as required. | |
Text | It allows you to select Independent variables. |
| |
Number of Clusters | It allows you to enter the number of clusters you want to create. | The default value is 3. | |
Advanced | Threshold | The default value is 0.5. | |
Branching Factor | It allows you to enter the number of child nodes that can be created at each node. | The default value is 50. | |
Example of Incremental Learning
Consider a dataset of Musical Instruments review. A snippet of input data is shown in the figure given below.
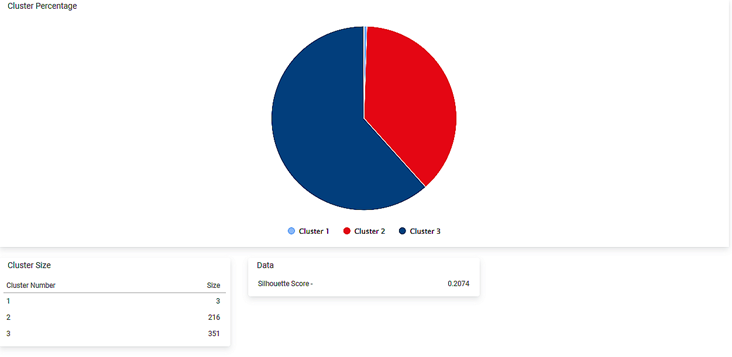
After using the Incremental Learning, the following results are displayed.
As seen in the above figure, the data is divided into three clusters. A pie chart of the clusters, each cluster's size, and the Silhouette Score are displayed.
Table of Contents