| Categorical Naive Bayes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Description | The categorical Naïve Bayes algorithm is suitable for categorically discrete values like Weather Prediction, and Medical Diagnosis. It is the simplest and fastest classification algorithm. | ||
Why to use | It is the simplest and fastest algorithm for a large chunk of textual data. | ||
When to use | When you want to process discrete features that are categorically distributed on a large amount of data. | When not to use | When your dataset does not contain a categorical dependent variable |
Prerequisites | – | ||
Input | A dataset with one categorical dependent variable. | Output |
|
Statistical Methods Used |
| Limitations |
|
The categorical Naive Bayes test is located under Machine Learning ( ) in Classification, on the left task pane. Alternatively, use the search bar for finding the Categorical Naive Bayes test feature. Use the drag-and-drop method or double-click to use the algorithm in the canvas. Click the algorithm to view and select different properties for analysis.
Properties of Categorical Naive Bayes test
The available properties of the Categorical Naive Bayes test are shown below.
The table below describes the different properties of the Categorical Naive Bayes Test.
Field | Description | Remark | |
|---|---|---|---|
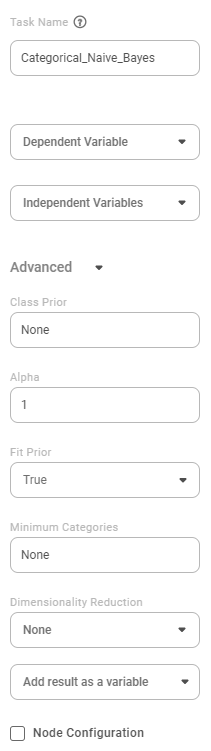
Task Name | It is the name of the task selected on the workbook canvas. |
| |
Dependent Variable | It allows you to select the categorical (discrete) variable. | Any one of the available binary variables can be selected. | |
Independent Variables | It allows you to select discrete features that are categorically distributed variables and numerical variables. |
| |
Advanced | Class Prior | It is the prior probabilities of the classes. |
|
Alpha | It allows you to enter the alpha value or a significance level |
| |
Fit Prior | It allows you to consider the data partially that fits in the memory. | The default is True. | |
Minimum Categories | It is the categories per feature. |
| |
Dimensionality Reduction | It allows you to select the dimensionality reduction technique. |
| |
Add result as variable |
|
| |
Node Configuration | It allows you to select the instance of the AWS server to provide control over the execution of a task in a workbook or workflow. | For more details, refer to Worker Node Configuration. | |
Example of Categorical Naive Bayes
As a manager, you want to shortlist the employees who are willing for business travel based on age and education. An input data snippet is displayed below.
We apply Categorical Naive Bayes to the input data by selecting two independent columns. The chosen values are given below.
Property | Value |
Task Name | Categorical_Naive_Bayes |
Dependent Variable | Business Travel |
Independent Variables | Age, Education |
Class Prior | None |
Alpha | 1 |
Fit Prior | True |
Minimum Categories | None |
Dimensionality Reduction | None |
Add Result as variable | None |
The result page displays the following sections.
Section 1 –
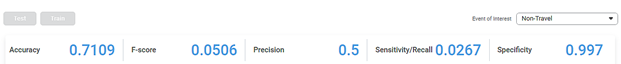
In the top right corner, the categorical variable's different options are displayed. When you select the different values, the following calculated statistical variables are displayed. The first option appears as the default selected option.
- Accuracy – This value represents the accuracy of predictions on the model.
- F-Score – This value represents the accuracy of predictions on the selected categorical variable.
- Precision – This value represents the number of false positives.
- Sensitivity/Recall – This value represents the number of positive instances.
- Specificity – This value represents the selected categorical value's ability to predict true negatives.
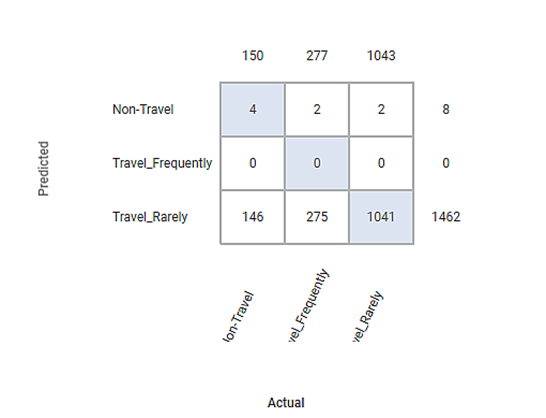
Section 2 – Confusion Matrix
Following is the confusion matrix for the specified categorical variable. It contains predicted values and actual values for the category.
- The shaded diagonal cells show the correctly predicted categories. For example, all 1041 employees in the Travel_Rarely category are correctly predicted.
- The remaining cells indicate the wrongly predicted categories. For example, 2 employees in the Non-Travel category are wrongly predicted.
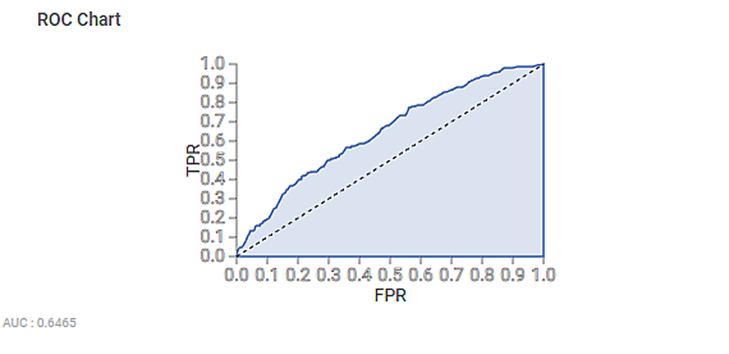
Section 3 – ROC chart
The Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Chart for the Business Travel is given below. ROC curve is a probability curve that helps in the measurement of the performance of a classification model at various threshold settings.
- ROC curve is plotted with a True Positive Rate on the Y-axis and a False Positive Rate on the X-axis.
- We can use ROC curves to select possibly the most optimal models based on the class distribution.
- The dotted line is the random choice with a probability equal to 50%, an Area Under Curve (AUC) equal to 0.64, and a slope equal to 1.
- In the above graph, the ROC curve is very close to the dotted line.
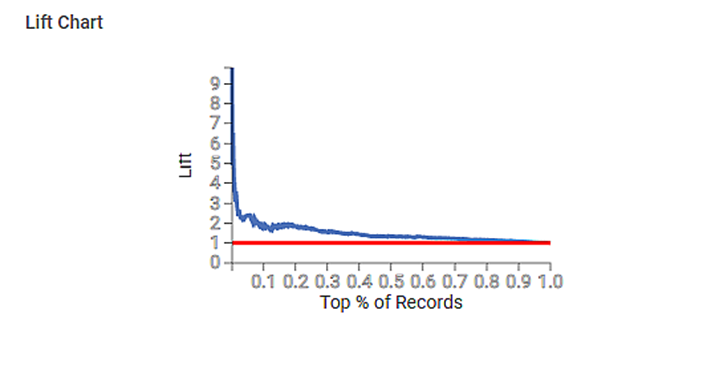
Section 4 – Lift Chart
The Lift Chart obtained for the Business Travel is given below. A lift is the measure of the effectiveness of a model. It is the ratio of the percentage gain to the percentage of random expectation at a given decile level. It is the ratio of the result obtained with a predictive model to that obtained without it.
- A lift chart contains a lift curve and a baseline.
- It is expected that the curve should go as high as possible towards the top-left corner of the graph.
- Greater the area between the lift curve and the baseline, the better the model.
- In the above graph, the lift curve remains above the baseline up to 30% of the records and then becomes parallel to the baseline.
Table of contents